Spine surgeon Anders Cohen puts a lot of stock in patients' expectations of pain relief. He prefers to operate only on those who "grab you by the collar and say, `I can't take it anymore.'"
New brain research proves doctors like Cohen are onto something: Pessimism can override the effectiveness of even powerful treatments.
 Full Story
Full Story
The more advanced degrees a person has, the lower their blood pressure, a study published online has found.
An analysis of some 4,000 patient records from the 30-year Framingham Offspring Study found that, controlling only for age, women with 17 years or more of education -- a master's degree or doctorate -- had systolic blood pressure readings 3.26 millimeters of mercury lower than female high school drop-outs.
 Full Story
Full Story
Most people put one in front of the other as a most basic way to get around, though they often come in handy to kick a ball, ride a bicycle or dance a jig -- maybe even walk a tightrope.
But in Asia, feet are far more than just the two pins that keep us upright and get us from A to B -- they can lead people into a cultural minefield.
 Full Story
Full Story
Hot flashes that bedevil many women in menopause might actually be a good thing, depending on when they strike, according to new data from a long-running government study.
Women who had hot flashes at the start of menopause but not later seemed to have a lower risk for heart attack and death than women who never had hot flashes, or those whose symptoms persisted long after menopause began.
 Full Story
Full Story
Organ traffickers in China could face the death penalty under a draft law being reviewed by the country's top legislature, state media reported Thursday.
Those convicted of "forced organ removal, forced organ donation or organ removal from juveniles" could face the same punishment as for homicide, which ranges from 10 years in prison to execution, Xinhua news agency said.
 Full Story
Full Story
Two medical investigations published on Tuesday have strengthened arguments that modest daily consumption of alcohol is good for the heart and the blood system.
People who drink alcohol in moderate amounts -- equivalent to about one drink a day or less -- are between 14 and 25 percent less likely to develop cardiovascular disease than counterparts who drink no alcohol at all, they said.
 Full Story
Full Story
U.S. scientists said Sunday there is strong evidence linking oral sex to cancer, and urged more study of how human papilloma viruses may be to blame for a rise in oral cancer among white men.
In the United States, oral cancer due to HPV infection is now more common than oral cancer from tobacco use, which remains the leading cause of such cancers in the rest of the world.
 Full Story
Full Story
U.S. researchers looking at how stress affects the gut stumbled upon a potent chemical that caused mice to regrow hair by blocking a stress-related hormone, said a study on Wednesday.
While the process has not yet been tested in humans, it grew more hair in mice than minoxidil, the ingredient in Rogaine, a popular treatment for baldness, said the study in the online journal PLoS One.
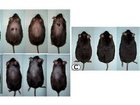 Full Story
Full Story
Almost 10,000 infants and toddlers are hurt in crib and playpen accidents each year, according to the first nationwide analysis of emergency room treatment for these injuries.
Most injuries were from falls in toddlers between ages 1 and 2 — generally old enough to attempt climbing out of a crib or playpen.
 Full Story
Full Story
Up to 10 percent of rice grown in China is contaminated with harmful heavy metals stemming from pollution linked to the nation's rapid industrialization, a report said.
This week's edition of the New Century magazine cited studies showing that large amounts of Chinese rice have been tainted with heavy metals like cadmium for years but that little has been done to highlight the dangers.
 Full Story
Full Story



