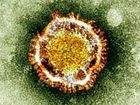
Asian countries should keep their guard against the deadly Middle East respiratory virus, although it is unlikely to spread to the region, a World Health Organization expert said Thursday.
The Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) appears to be less infectious than originally thought even though it has already killed 287 people, said Mark Jacobs, WHO's director for communicable diseases in the Western Pacific.
 Full Story
Full Story
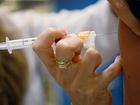
A vaccine that protects against four strains of the human papillomavirus, which can lead to cervical cancer, does not increase the risk of blood clots in women, researchers said Tuesday.
The findings in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) are based on 500,000 girls and women aged 10 to 44 who received the HPV vaccine between 2006 and 2013.
 Full Story
Full Story
Twenty-five percent more children are falling ill with TB than the U.N. had thought, with more than 650,000 hit by the disease each year in the 22 worst affected countries, specialists said Wednesday.
Reporting in The Lancet, they said that about 53 million children under 15 are living with latent TB infection, a condition that can develop into active TB at any time.
 Full Story
Full Story
Federal investigators are probing how vials of smallpox made their way into a storage room at a Food and Drug Administration lab near the U.S. capital, health authorities said Tuesday.
 Full Story
Full Story
The number of people believed to have died from Ebola in west Africa has jumped to 518, the World Health Organization said Tuesday.
The U.N. health agency said that 50 new cases -- 25 of them fatal -- had been reported between July 3-6 by health authorities in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone.
 Full Story
Full Story
U.S. regulators on Monday put an experimental immunotherapy agent on the fast track to market approval, after 89 percent of leukemia patients in early trials saw their cancers disappear.
The personalized immunotherapy known as CTL019 was developed by the University of Pennsylvania and was designated a "breakthrough therapy" by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
 Full Story
Full Story
A British study has identified blood proteins that appear in patients subsequently diagnosed with Alzheimer's, raising hopes of a test that could help the search for a cure.
There is currently no cure for the brain-wasting disease, the most common form of dementia, which Alzheimer's Disease International estimates affects 44 million people worldwide, a figure set to triple by 2050.
 Full Story
Full Story
A mold outbreak last year in some U.S. containers of Chobani yogurt may have been more dangerous than the company initially acknowledged, according to a scientific study out Tuesday.
The yogurt company issued a voluntary recall of certain products with "best by" dates between September and October 2013 from its Idaho plant.
 Full Story
Full Story
In 1992, a pair of scientists had a brainwave: how about inserting genes into rice that would boost its vitamin A content?
By doing so, tens of millions of poor people who depend on rice as a staple could get a vital nutrient, potentially averting hundreds of thousands of cases of blindness each year.
 Full Story
Full Story
Many cases of Ebola in Sierra Leona may be going undetected, grassroots doctors warned in The Lancet on Saturday as they highlighted the impoverished country's problems in combating the virus.
The journal published the letter on the heels of ministerial talks in Ghana, where a senior U.N. health official on Thursday said the outbreak in West Africa, the worst in the history of Ebola, may persist for several more months.
 Full Story
Full Story



