Peru on Monday reported its first cases of the chikungunya virus, in two people who recently traveled to the Dominican Republic, authorities said.
Health ministry director Henry Rebaza said the man and woman who were diagnosed in Lima had recently traveled to the Dominican Republic, a popular Caribbean vacation spot where the virus has been detected.
 Full Story
Full Story
An epidemic of the deadly Ebola virus in West Africa is now "out of control" with more than 60 outbreak hotspots, the medical charity Doctors Without Borders (MSF) said on Monday.
"The scale of the current Ebola epidemic is unprecedented in terms of geographical distribution, people infected and deaths," MSF said in a statement.
 Full Story
Full Story
The British army has a global reputation for efficiency and performance, but new figures published on Sunday suggest that its soldiers might be getting a little soft.
More than 32,000 soldiers failed a basic fitness test at some point in the past three years, and more than 22,000 were found to be overweight and at risk of health problems, according to Ministry of Defense figures.
 Full Story
Full Story
Two million children under five die each year in central and western Africa, accounting for almost a third of all deaths worldwide in that age range, the U.N. children's agency said Sunday.
Progress in reducing child mortality has not affected the overall number of deaths because of "enormous" population growth, said Manuel Fontaine, UNICEF's director for the region.
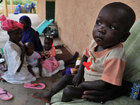 Full Story
Full Story
Scientists said Sunday they may have unraveled how chronic stress leads to heart attack and stroke: triggering overproduction of disease-fighting white blood cells which can be harmful in excess.
Surplus cells clump together on the inner walls of arteries, restricting blood flow and encouraging the formation of clots that block circulation or break off and travel to another part of the body.
 Full Story
Full Story
A California study out Monday found that pregnant women who lived near farms where pesticides are applied had a two-thirds higher risk of having children with autism.
The findings in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives examine the association between living near commercial pesticide applications and having offspring with autism, but do not show cause-and-effect.
 Full Story
Full Story
The recent rapid spread of Ebola in three countries in West Africa has come in part because efforts to contain the deadly virus have been relaxed, Pierre Formenty, a World Health Organisation specialist, told Agence France Presse on Saturday.
 Full Story
Full Story
A sharp rise in new HIV infections in the Middle East and North Africa is a worrying trend, despite some positive developments, UNAIDS chief Michel Sidibe told Agence France Presse on Friday.
While the epidemic remains very "concentrated" within the region, with homosexuals, sex workers, migrants and drug addicts comprising the vast majority of cases, the Arab world has seen a dramatic increase in new cases in recent years.
 Full Story
Full Story
Sierra Leone, one of three neighboring west African countries facing an Ebola epidemic, has stepped up measures to fight the highly contagious and deadly disease, the health minister has said.
Miatta Kargbo said Thursday that the number of registered cases of hemorrhagic fever had risen to 246. Of these, 103 were confirmed to be Ebola and 26 had died.
 Full Story
Full Story
Once doomed to a life of darkness, dozens of people stricken by retinal diseases are rediscovering a world of light as scientists push ahead on cures for blindness.
Already, bionic retinas enable blind people to "see" sidewalks, doorways and even oversized text while gene therapy has allowed a small boy to put away his white cane and take up Little League baseball.
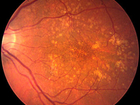 Full Story
Full Story



